Harvest is one of the most important parts of your hemp season. It is the…
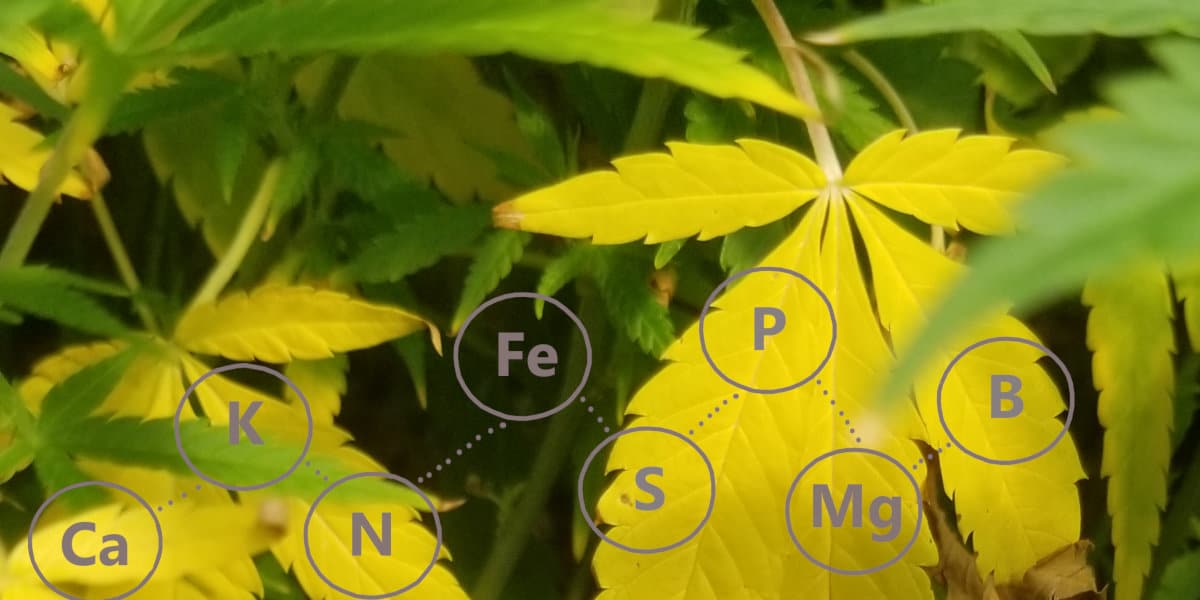
Nutrient Deficiency Troubleshooting
This is a troubleshooting guide to help identify potential nutrient deficiencies while waiting for feedback from your state’s extension office or other identification service. Let’s take a look at the nutrients necessary for plant growth and development.
Primary/Macronutrients: Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Potassium
Secondary nutrients: Calcium, Magnesium, Sulfur
Micronutrients: Boron, Chloride, Copper, Iron, Manganese, Molybdenum, Zinc, Nickel
Micronutrients are often present in your water or soil (if applicable), however, micronutrient deficiencies can still occur, particularly iron. For this reason, water and soil should always be tested prior to planting.

As soon as you notice an issue with your plants, immediately note where on the plant it first occurred. For example, all anomalies in color, shape, and rate of development on what part of the leaf, what part of the plant (old or new growth). Where symptoms first begin is important to identification. Nutrient deficiencies often show up symmetrically on the leaf so if signs are asymmetric, the issue may be something else like disease or insect pests.
Next, check pH. Make sure the pH of your grow media, irrigation, and/or fertigation is properly regulated for your plant and nutrients. Often plants will exhibit signs of deficiency if pH is too high or too low, even when adequate amounts of nutrients are supplied because some nutrients aren’t available at certain pH levels. This is known as nutrient lockout.
The ideal pH for your cannabis grow will be between 5.8 and 6.0. Most necessary nutrients are available at different levels within this range so allowing fluctuation within the range helps to provide the highest nutrient availability possible.


Key Terms
Chlorosis – yellowing of leaf parts, can show up in different areas and patterns
Mobile – nutrient is able to move through the plant and will move from older tissue at base of plant to younger tissue at tops of plant
Immobile – nutrient does not move through plant, deficiencies shown in new growth
Partially mobile – Some mobility potential
Leaf abscission – leaf shedding
Necrosis – plant parts darkening and wilting, dying off, may appear as burning
Interveinal – space in between the veins of the leaves
Leaf margins – the edges of the leaves
See the chart below to identify specific symptoms and the nutrients they are associated with.
Nitrogen (N) - Mobile
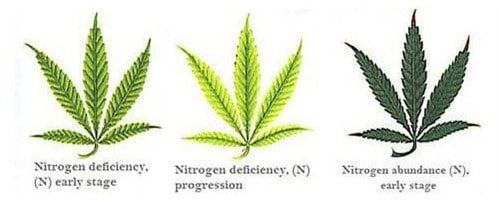
Function: Visually gives plant green color
Deficiency Symptoms: Uniform chlorosis of older leaves first, early flowering, stunted growth, and leaf abscission
Additional Notes: One of the most common deficiencies in Cannabis
Phosphorus (P) - Mobile
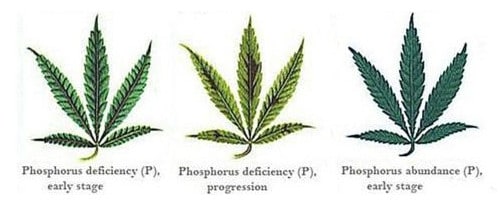
Function: Root growth and flower production
Deficiency Symptoms: Chlorosis on older leaves, potential purple coloration on leaves (can also be caused by other stressors)
Additional Notes: Excess Phosphorus can lead to zinc and iron lockout, this is a more common deficiency in cold temperatures
Potassium (K) - Mobile
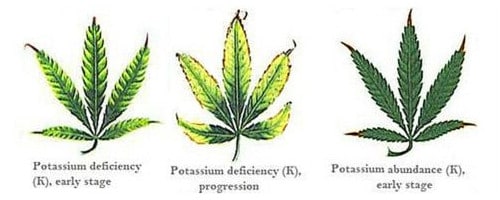
Function: Assists with plant’s ability to produce sugars, flower development
Deficiency Symptoms: Chlorosis quickly leading to necrosis around leaf margins and through leaf, excessive stretching and brittle stems
Additional Notes: Potassium is crucial for terpene production
Calcium (Ca) - Immobile

Function: Cell division and formation, sturdy structure of plants and nutrient uptake, flower formation
Deficiency Symptoms: New growth is stunted with leaf distortion at top of plants, brown spots on leaves, and incomplete flower formation (blossom end rot in tomatoes)
Additional Notes: Calcium deficiency makes plants more prone to disease and insect pests
Magnesium (Mg) - Mobile
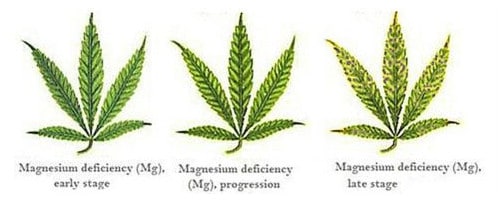
Function: Chlorophyll formation
Deficiency Symptoms: Interveinal chlorosis in old leaves
Additional Notes: Often shows up
Sulfur (S) - Immobile/partially mobile
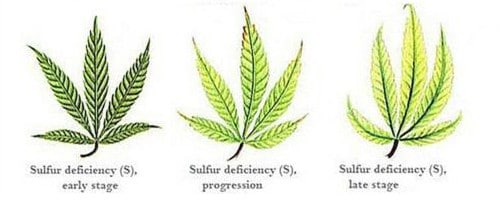
Function: Assists in nitrogen fixation, and formation of chlorophyll
Deficiency Symptoms: Can appear similar to Mg, uniform chlorosis through the entire plant but can be exaggerated in younger leaves
Additional Notes: Plants are more at risk in cold soil
Boron (B)

Function: New growth formation, and strength of plant
Deficiency Symptoms: Leaf distortion, flower stunting with stem breakage, short and thick root development, short internodes and thick leaves, die-off of new growth
Additional Notes: Often occurs due to under watering or low humidity
Chlorine (Cl)

Function: Aids in photosynthesis and water movement through the plant
Deficiency Symptoms: Inteveinal chlorosis and necrotic spots on younger leaves
Additional Notes: Deficiencies are rare, but toxicity shows up as burning leaf margins
Copper (Cu)

Function: New flower growth and development
Deficiency Symptoms: Leaf tip discoloration or “burning” and weak stems
Additional Notes: Not available to plants at pH extremes
Iron (Fe)
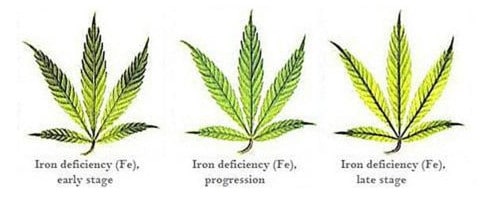
Function: Chlorophyll production and plant metabolism
Deficiency Symptoms: Chlorosis specifically on younger leaves
Additional Notes: Can be caused by over watering
Manganese (Mn)
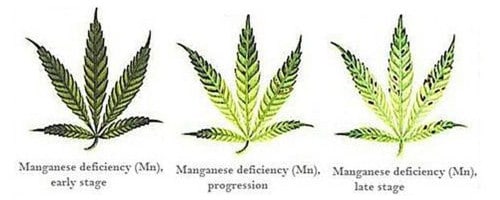
Function: Photosynthesis, respiration, and root elongation
Deficiency Symptoms: Interveinal chlorosis at top of plant leading to some necrosis and light tan spots
Additional Notes: Most common cause is high pH
Molybdenum (Mb) - Partially mobile
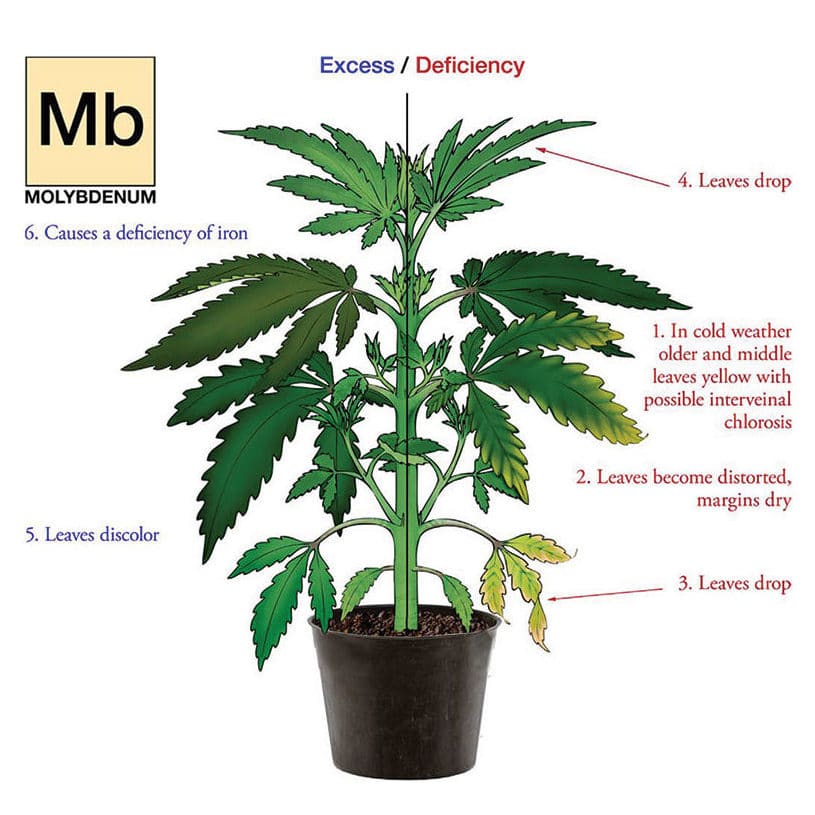

Function: Processing nitrogen
Deficiency Symptoms: Chlorosis in thin band around leaf margins
Additional Notes: Molybdenum becomes locked out at pH below 5.5
Zinc (Zn)
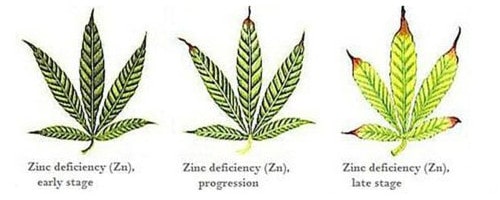
Function: Fundamental in building plant structures and growth regulating hormones
Deficiency Symptoms: Chlorosis of new growth spreading from leaf tip to base, and stunted plants
Additional Notes: Excess zinc can lockout iron
Nickel (Ni)
Function: Helps plant metabolize and use nitrogen as urea, and assists in iron uptake
Deficiency Symptoms: Necrosis on leaf tips
Additional Notes: Essential for Fe uptake


